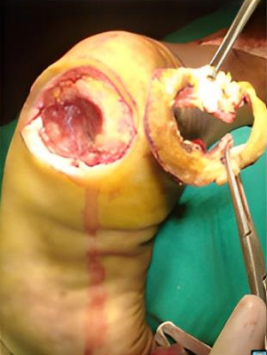
Reverse Sural Flap for Post Traumatic Soft-Tissue Defects of Leg Ankle and Heel – Our Experience
Main Article Content
Abstract
Treatment and management of severe wound defects related to leg and ankle injury are sometimes very challenging. Microsurgical repair is one of the best options. However, it is a bit difficult and hectic to transfer free tissue from other body parts due to donor site morbidity, longer duration, bulky tissue, recipient vessel risks, sophisticated expertise, and high costs of the equipment and treatment. Meanwhile, the reverse Sural flap has been considered as the ultimate method of tissue restoration. This study was conducted in 36 patients who were admitted to our Centre in the Department of Plastic Surgery. The patients had multiple ankle and leg tissue defects. After the diagnosis, our plan involved surgical debridement, tendon repair if involved, and reverse sural flap rotation. Despite the difficulties in the working environment and advanced learning experience, our patients fully recovered within 3 weeks. Proving that reverse sural flap is one of the few available options in the protection of vital structures such as tendons, nerves, bones, in the distal areas of the leg, ankle, and foot especially when we lack a strong microsurgery team and equipment.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
Taylor, G. I., and ROLLIN K. Daniel. "The anatomy of several free flap donor sites." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 56.3 (1975): 243-253.
Ponten, Bengt. "The fasciocutaneous flap: its use in soft tissue defects of the lower leg." British Journal of Plastic Surgery 34.2 (1981): 215-220.
Baumeister, Steffen P., et al. "A realistic complication analysis of 70 sural artery flaps in a multimorbid patient group. "Plastic and reconstructive surgery 112.1 (2003): 129-140.
Montegut, W. J., and R. J. Allen. "Sural artery perforator flap as an alternative for the gastrocnemius myocutaneous flap." Proceedings from the 90th Annual Scientific Assembly of the Southern Medical Association. 1996.
Schmidt, Karsten, et al. "The distally based adipofascial sural artery flap: faster, safer, and easier? A long-term comparison of the fasciocutaneous and adipofascial method in a multimorbid patient population." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 130.2 (2012): 360-368.
Masquelet, A. C., M. C. Romana, and G. Wolf. "Skin island flaps supplied by the vascular axis of the sensitive superficial nerves: anatomic study and clinical experience in the leg." Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 89.6 (1992): 1115-1121.
Yadav, Sankalp, Gautam Rawal, and Mudit Baxi. "Vacuum assisted closure technique: a short review." The Pan African Medical Journal 28 (2017).
Ciofu, R. N., et al. "Reverse sural flap for ankle and heel soft tissues reconstruction." Journal of Medicine and Life 10.1 (2017): 94.
Masquelet, A. C., M. C. Romana, and G. Wolf. "Skin island flaps supplied by the vascular axis of the sensitive superficial nerves: anatomic study and clinical experience in the leg." Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 89.6 (1992): 1115-1121.
Aoki, Shimpo, et al. "Clinical and vascular anatomical study of distally based sural flapv." Annals of Plastic Surgery 61.1 (2008): 73-78
Zhang, Fahui, et al. "Distally based sural neuro-lesser saphenous veno-fasciocutaneous compound flap with a low rotation point: microdissection and clinical application." Annals of plastic surgery 62.4 (2009): 395-404.
De Blacam, Catherine, et al. "Risk factors associated with complications in lower-extremity reconstruction with the distally based sural flap: a systematic review and pooled analysis." Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 67.5 (2014): 607-616.
Schaverien, Mark, and Michel Saint-Cyr. "Perforators of the lower leg: analysis of perforator locations and clinical application for pedicled perforator flaps." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 122.1 (2008): 161-170.
Chang, Shi‐Min, et al. "Distally based sural fasciomyocutaneous flap: anatomic study and modified technique for complicated wounds of the lower third leg and weight bearing heel." Microsurgery: Official Journal of the International Microsurgical Society and the European Federation of Societies for Microsurgery 29.3 (2009): 205-213.
Eser, Cengiz, et al. "A convenient flap for repairing the donor area of a distally based sural flap: gastrocnemius perforator island flap." Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 69.8 (2016): 1109-1115.
Blondeel, Phillip N., et al., eds. Perforator flaps: anatomy, technique, & clinical applications. CRC press, 2013.
Olawoye, Olayinka Adebanji, et al. "The reverse sural artery flap for the reconstruction of distal third of the leg and foot." International Wound Journal 11.2 (2014): 210-214.
Ciofu, R. N., et al. "Reverse sural flap for ankle and heel soft tissues reconstruction." Journal of Medicine and Life 10.1 (2017): 94.
Levine, Jamie P., Lee LQ Pu, and Fu-Chan Wei, eds. Reconstructive Surgery of the Lower Extremity. Quality Medical Publishing, Incorporated, 2013.
Huisinga, R. L., et al. "The distally based sural artery flap." Annals of plastic surgery 41.1 (1998): 58-65.
Tan, Onder, Bekir Atik, and Mehmet Bekerecioglu. "Supercharged reverse‐flow sural flap: A new modification increasing the reliability of the flap." Microsurgery: Official Journal of the International Microsurgical Society and the European Federation of Societies for Microsurgery 25.1 (2005): 36-43.
Kneser, Ulrich, et al. "Delayed reverse sural flap for staged reconstruction of the foot and lower leg." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 116.7 (2005): 1910-1917.
Baumeister, Steffen P., et al. "A realistic complication analysis of 70 sural artery flaps in a multimorbid patient group." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 112.1 (2003): 129-140.
Hallock, Geoffrey G. "Anatomic basis of the gastrocnemius perforator-based flap." Annals of plastic surgery 47.5 (2001): 517-522.
Roberts, Haydn J., and Gregory L. DeSilva. "Can sural fasciocutaneous flaps be effective in patients older than 65?." Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 478.4 (2020): 734.
Mehrotra, Sandeep. "Perforator-plus flaps: a new concept in traditional flap design." Plastic and reconstructive surgery." 119.2 (2007): 590-598.
Chang, Shi-Min, et al. "Distally based perforator propeller sural flap for foot and ankle reconstruction: a modified flap dissection technique." Annals of plastic surgery 72.3 (2014): 340-345.
Kim, Kyu Jin, et al. "A comparison of fasciocutaneous and adipofascial methods in the reverse sural artery flap for treatment of diabetic infected lateral malleolar bursitis." Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 27.1 (2019): 2309499019828546.
Hasegawa, Morimasa, et al. "The distally based superficial sural artery flap." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 93.5 (1994): 1012-1020.
Chang, Shi‐Min, et al. "Distally based sural fasciomyocutaneous flap: anatomic study and modified technique for complicated wounds of the lower third leg and weight bearing heel." Microsurgery: Official Journal of the International Microsurgical Society and the European Federation of Societies for Microsurgery 29.3 (2009): 205-213.
Aydin, Osman E., et al. "Nerve sparing‐distally based sural flap." Microsurgery 31.4 (2011): 276-280.
Pirwani, Mehtab A., Saeed Samo, and Yunis H. Soomro. "Distally based sural artery flap: A workhorse to cover the soft tissue defects of lower 1/3 tibia and foot." Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 23.1 (2007): 103.
Baumeister, Steffen P., et al. "A realistic complication analysis of 70 sural artery flaps in a multimorbid patient group." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 112.1 (2003): 129-140.